Boosting naturally occurring retinoic acid - How does it work?
NovoRetin™, our new natural alternative to retinol, can increase the amount of naturally occurring retinoic acid in the skin, resulting in retinol-like effects without the need to apply retinol on the skin.
The increase of retinoic acid in the skin is the result of the inhibition of the enzyme CYP26A1 by NovoRetin™. But what exactly does this mean? Let’s start from the beginning.
Retinol (vitamin A1) is an essential fat-soluble vitamin that cannot be synthesized by the human body but is absorbed from food. Together with structurally related molecules, retinol belongs to the family of retinoids. Retinol is required for many biological processes in the human body. In the skin, it has modulatory functions on keratinocyte proliferation, and thereby positive effects on wound healing and skin barrier function. Retinol is also well-known in the cosmetic field due to its strong anti-aging properties when being applied topically. Furthermore, various retinoids are used to treat pathological skin conditions, including acne, psoriasis, and ichthyosis. However, it is important to know that retinoids are not only used topically in cosmetic or pharmaceutical treatments, but retinol itself also occurs naturally in the skin.
The major active metabolite of retinol is retinoic acid. The activity of retinol is mediated mainly through binding of retinoic acid to specific receptors called retinoid X receptors (RXR) and retinoic acid receptors (RAR) in the cell nucleus and thereby regulating the expression of various target genes. The altered expression of these genes in turn leads to the positive effects on the skin, such as skin rejuvenation and improvement of impure skin, that we all know from classical retinol treatments.
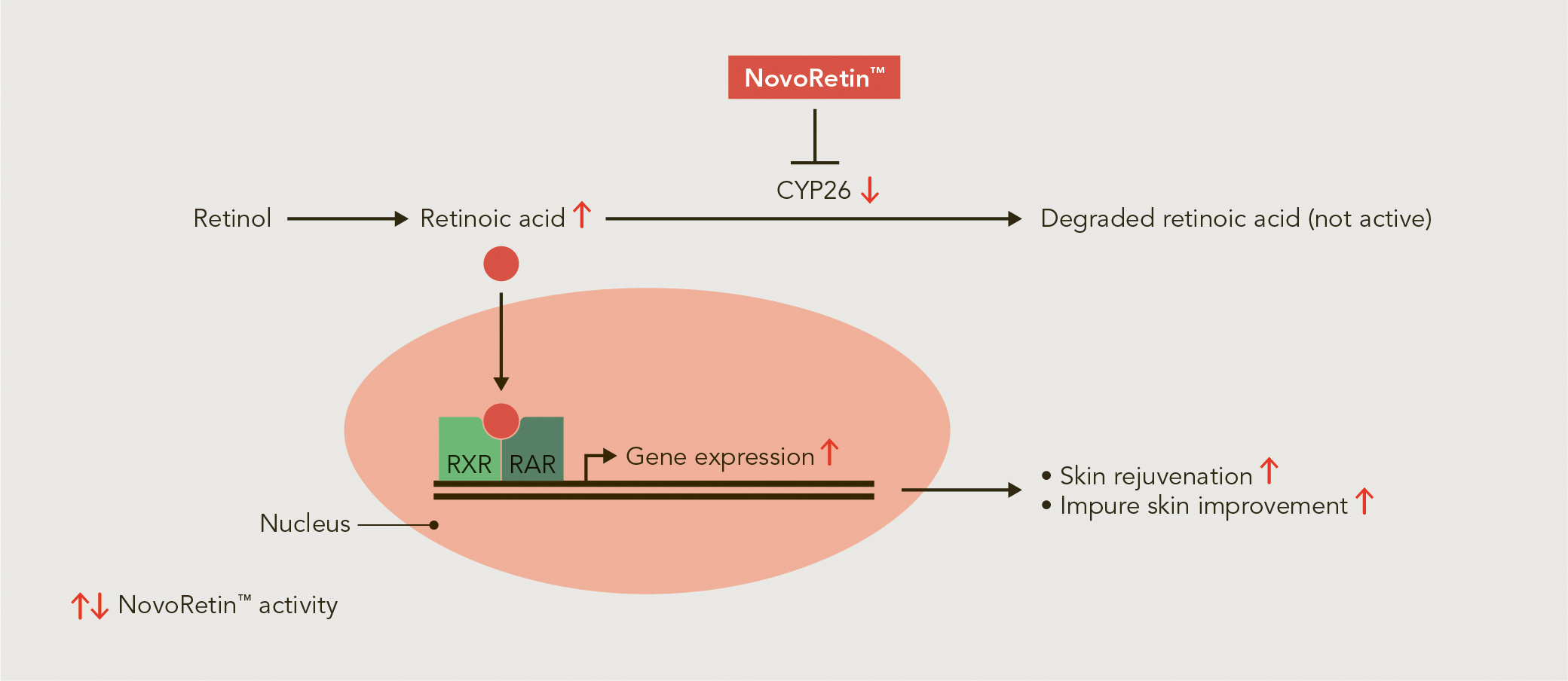
In our cells, retinoic acid is rapidly degraded by cytochrome P450 family 26 (CYP26) enzymes, which transform retinoic acid into the non-active form of hydroxy-retinoic acid. The presence of retinoic acid even enhances the expression of CYP26 enzymes, which means that retinoic acid can induce its own degradation. Thus, relatively high concentrations of retinoic acid are necessary to result in gene expression effects despite the constant degradation of retinoic acid.
A strategy to overcome this problem and to prevent the degradation of naturally occurring retinoic acid is to inhibit the CYP26 enzymes. Indeed, as shown in several published studies, specific synthetic CYP26 inhibitors have demonstrated efficacy for several dermatological disorders with better tolerability than previous retinoid therapies. This means that it is possible to increase the levels of naturally occurring retinoic acid within the skin by inhibiting its degradation. Based on this idea from the pharma industry, we have developed NovoRetin™ as a natural, plant-based alternative to inhibit the activity of CYP26A1, the CYP26 subtype in the skin, for cosmetic applications.
By inhibiting CYP26A1, NovoRetin™ retains the naturally occurring retinoic acid in the skin, resulting in retinol-like effects without the need to apply retinoids topically on the skin. Thus, formulation challenges due to the instability of retinoids and the negative side effects of topical retinol treatments are completely avoided.
If you have further questions concerning NovoRetin™, please feel free to contact us.









